

Serious conditions can occur because of the occlusive phase of the disease. A difference in blood pressure between the arms and the legs.Tenderness above the affected arteries.ĭuring the occlusive phase, symptoms include:.In the first phase, about half of all patients develop one or more of the following symptoms: Later, during the occlusive phase, blood vessels narrow. In the first phase, the blood vessels become inflamed. Symptoms depend on the phase of the disease. Atherosclerosis, or hardening of the arteries, is the most common cause of aortic arch disease. Aneurysms are a life-threatening condition because they can rupture. Narrowing can reduce blood flow, and weakening can lead to the formation of an aneurysm, or abnormal bulge, in the artery wall. Takayasu's mostly affects Asian females between the ages of 10 and 30.Īortic arch conditions eventually block the blood vessels that branch off the aorta, leading to decreased blood flow to areas of the body. These abnormalities can reduce blood flow to vital organs.Īortic arch disease can result from blood pressure changes, clots, trauma, a congenital disorder (one that is present from birth), or Takayasu's arteritis, an autoimmune disorder that inflames the aorta and the pulmonary artery (the main artery of the lung). Aortic arch conditions are abnormalities in the structure of the arteries that branch off the top of the aorta. It runs from the heart, through the chest, and down into the abdomen. If you or someone you love might benefit from this type of surgery, make an appointment today with one of WakeMed’s specialized cardiologists.The aorta is the body's largest artery. The specially trained surgeons at WakeMed’s Center for Proximal Aortic Surgery perform all types of advanced aortic valve repair surgeries. The Center also treats aortic valve diseases such as aortic stenosis, aortic insufficiency and bicuspid aortic valves. Proximal descending thoracic aortic aneurysms.In addition to treating native aortic infections (including endocarditis) and congenital aortic disease, the Center for Proximal Aortic Surgery treats many types of aortic aneurysms, including: Stent graft/minimally invasive endovascular surgeryĬonditions Treated by the Center for Proximal Aortic Surgery.Multi-modality imaging of a variety of complex thoracic aortic conditions.Valve-preserving operations for aortic root aneurysms.Minimally invasive stent-grafts for selected descending thoracic aortic aneurysms.Our specialists are able to provide the latest in advanced surgical options, including:
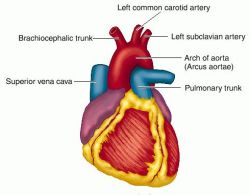
Advanced cardiopulmonary perfusion techniques.Valve repair and valve-sparing aortic roots.Percutaneous and transcatheter valve therapies.To achieve optimal patient outcomes, our clinicians use cutting-edge technologies that include: The cardiovascular surgeons at WakeMed’s Center for Proximal Aortic Surgery perform the most advanced surgeries available. However, surgical repair of a thoracic aortic aneurysm is usually performed if the aneurysm is large enough to carry a significant risk of rupture or dissection-or if the aneurysm is causing symptoms. Smaller thoracic aortic aneurysms are typically managed with blood pressure control and regular follow-up imaging. Treating Proximal Thoracic Aortic Diseases We ask patients to bring any previous studies with them, and we may order additional tests.īased on this information, our team recommends an individualized plan. We begin with an evaluation to understand the patient’s history of cardiovascular disease and hypertension, and the history of the aortic condition itself. Diagnosing Proximal Thoracic Aortic Diseases The cardiovascular surgeons at WakeMed’s Center for Proximal Aortic Surgery perform the most advanced surgeries to manage proximal aortic conditions such as aneurysms and valve disease, and are making strides in innovative research involving proximal aortic aneurysm surgery. An undetected and untreated aneurysm in the proximal thoracic aorta can be dangerous because it can burst and cause life-threatening internal bleeding. Made up of the ascending aorta, the aortic arch and the upper descending aorta, the proximal thoracic aorta plays a key role in receiving blood from the heart’s left ventricle, distributing blood to organs and tissues, and cushioning blood flow pulsations.Īn aneurysm is a balloon-like bulge in a weakened section of an artery wall. The proximal thoracic aorta is the part of the aorta-the body’s largest artery-that runs through the chest.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
